Identifying the Matters that Matter
Structure
The foundation for a well-structured system was set in place during FY 2011/12 and further refined during subsequent years. The core elements of our structure and approach are noted below:- Sustainability interests are addressed at each sector level and these heads form the Sustainability Governing Council. They work with and report to the Hayleys PLC Corporate Sustainability Team (CST). The CST is in charge of Group-wide sustainability initiatives (as opposed to sector-driven initiatives) and Group Sustainability Reporting
- The Sector Head (Group Management Committee Member) is responsible for the sustainability performance of his/her sector
- Both the Group Management Committee (GMC) and the Hayleys CST may approach the Chairman directly on sustainability-related issues, as the Chairman is at the apex of the Governing Structure.
The Identification Process
Relevant topics and indicators are those that echo the Group’s significant economic, environmental and social impacts. They are thus material, and recognised for their impact on the business of Hayleys Group and its key stakeholders.The following steps summarise the process we adopt to determine the materiality of topics and issues within the Hayleys Group:
- The CST conducts stakeholder mapping and materiality identification exercises with each Group sector
- Group sectors analyse current and potential issues and identify the impact on the business and stakeholders.
- Impacts are identified based on the consequences to stakeholders and the business value drivers, and the likelihood of such occurrence.
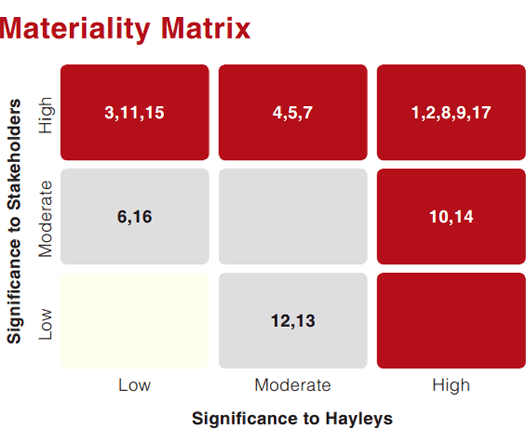
- An impact vs likelihood risk assessment matrix is plotted to identify the issues of high materiality. These issues could have a positive or negative impact on the business and its stakeholders.
- The CST conducts a review and prioritisation exercise to identify the Group Materiality Matrix
- The above lead to a Group Materiality Matrix in respect of risks that should be mitigated and opportunities that may be exploited.
| Aspect | Indicator | Significance to Hayleys | Significance to Stakeholders | |
| 1. | Economic Performance | G4-EC1 | H | H |
| G4-EC2 | ||||
| G4-EC3 | ||||
| 2. | Indirect Economic Impacts | G4-EC8 | H | H |
| 3. | Energy | G4-EN5 | L | H |
| 4. | Emissions | G4-EN15 | M | H |
| G4-EN16 | ||||
| G4-EN17 | ||||
| 5. | Effluents and Waste | G4-EN23 | M | H |
| 6. | Compliance | G4-EN29 | L | M |
| 7. | Anti-corruption | G4-SO3 | M | H |
| 8. | Compliance | G4-SO8 | H | H |
| 9. | Employment | G4-LA1 | H | H |
| G4-LA2 | ||||
| 10. | Labour/Management Relations |
G4-LA4 | H | M |
| 11. | Occupational Health and Safety |
G4-LA5 | L | H |
| G4-LA6 | ||||
| 12. | Training and Education | G4-LA9 | M | L |
| 13. | Investments | G4-HR1 | M | L |
| 14. | Child Labour | G4-HR5 | H | M |
| 15. | Product and Service Labelling |
G4-PR3 | L | H |
| 16. | Marketing Communications | G4-PR7 | L | M |
| 17. | Compliance | G4-PR9 | H | H |
Stakeholder Engagement
Conducting business successfully across the diversity of the Hayleys Group requires constant engagement and dialogue with stakeholders. Understanding the impacts and implications of our enterprise on these stakeholders, both internal and external and how they think and respond to issues of importance to them are vital for the long-term prosperity and well-being of both Hayleys and the stakeholder.We strive for inclusivity; we are committed to reflect at all stages of a process, the views and needs of all stakeholder groups. Stakeholder views are obtained through an engagement process that allows them to be expressed without fear or restriction. Inclusivity requires the consideration of ‘voiceless’ stakeholders including future generations and the environment. Key concerns raised by stakeholders are dealt with and addressed by sectors as applicable to them.
Our business sectors have various mechanisms for engaging with their stakeholders. Data on environmental and safety issues are compiled from operating data maintained by the various businesses, factories, hotels and other units of the Group. Data on social responsibility is obtained on-site.
The table below depicts the process followed by the Group on stakeholder engagement and identification of issues material to them and the Group:
Stakeholder Engagement
| Stakeholder | Process of Engagement and Frequency |
| Shareholders |
|
| Customers |
|
| Business Partners |
|
| Suppliers |
|
| Employees |
|
| Unions |
|
| Local Communities |
|
| Society/Pressure Groups/Competitors/Media |
|
| Government |
|
| Trade Associations |
|
Risk Management
Overview
Risk arises in all our business activities. Risk, in our context, is the probability of any negative occurrence that is caused by external or internal vulnerabilities that may be mitigated through pre-emptive action. Its significance is measured in terms of severity and the probability of occurrence.While risk cannot be completely eliminated we adopt measures to manage it. A structured and transparent enterprise risk management (ERM) process enables us to identify, manage and prepare for risks in an informed, controlled and transparent manner to achieve the optimum trade-off between risks and returns.
The Hayleys Group uses the COSO (Committee of Sponsoring Organisations of the Treadway Commission, www.aicpa.org) and established practices as the framework for ERM. This consists of identifying and profiling of significant risks, modelling and measuring risk, determining Group risk appetites, accepting/transferring/eliminating/sharing risk, measuring of performance including the benefits of risk diversification and monitoring execution of the process. It is about directing scarce resources to opportunities while taking cognisance of the risk - return trade off.
Risk Categories and Framework
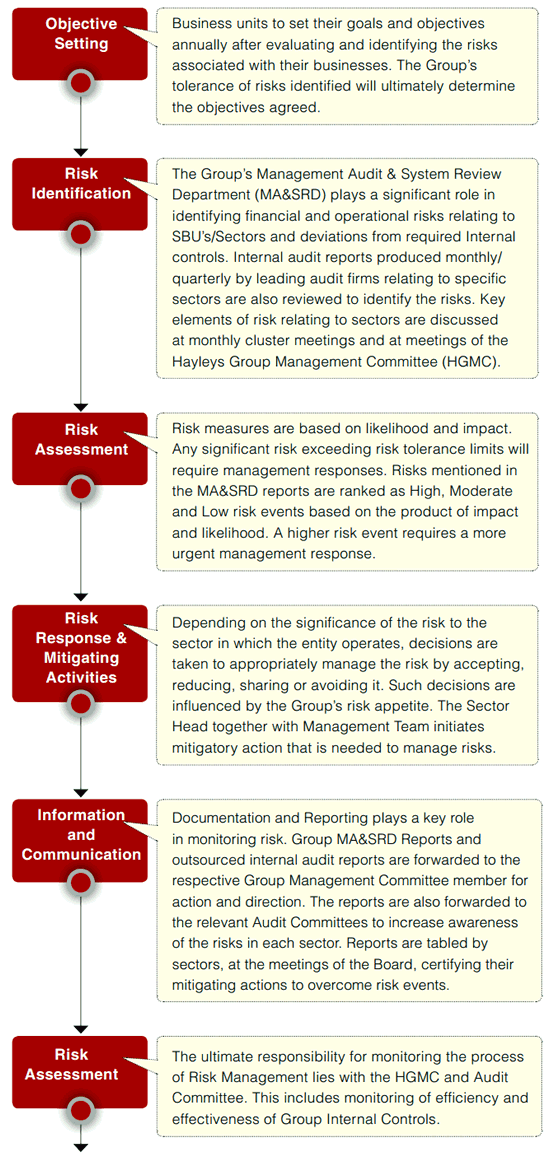
The Hayleys Group has a structured risk management process to address different risk categories: Strategic, Operational, Compliance and Financial.Risks and opportunities are identified by combining elements of a top-down and bottom-up approach. Risks are reported on a regular basis as part of the business performance management process. All relevant risks and opportunities are prioritised in terms of impact and likelihood, considering quantitative and/or qualitative aspects. The bottom-up identification and prioritisation process is supported by meetings/forums with the respective management at Sector and SBU Function level. The top-down element ensures that potential new risks and opportunities are discussed at management level and are included in the subsequent reporting process, if applicable. Reported risks and opportunities are analysed regarding potential cumulative effects and are aggregated at Sector, Cross-Sector/Company and SBU level.
Risk Management Framework
| Risks /Opportunities | ||||
| Strategic | Operational | Compliance | Financial | |
| Macroeconomic changes Changes in industry/market Acquisitions Growth emerging markets | Innovation process Value chain People Business disruption Reputation | Legal Tax Market practices Regulatory General business principles Internal controls Data privacy/product security | Treasury Accounting and reporting | |
| Corporate Governance | ||||
| Risk Management Framework (COSO) | ||||
Individual sectors nominate persons responsible for risk management at higher managerial levels, while risk management coordinators ensure that an effective system for early identification of risks is implemented and maintained at sector level. Group Internal Audit coordinates the identification and documentation of control risk areas throughout the Group, enhancing the risk management system and monitoring its effectiveness at regular intervals. In addition, during the year-end audit, the External Auditor issues a Management Letter and informs the Group Management Committee and the Board of Directors the outcomes of these evaluations. These outcomes are taken into account in the continuing enhancement of our risk management system.
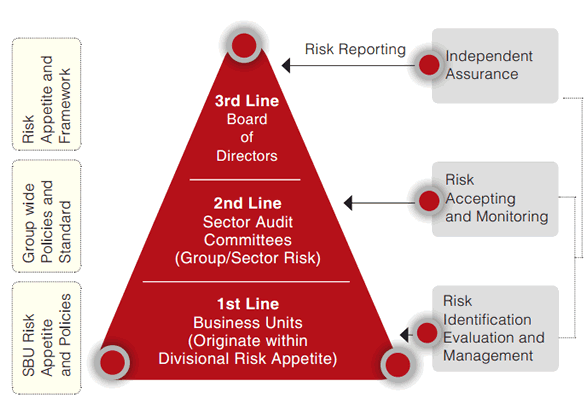
The 1st Line of Defence - Risk Identification, Risk Management and Self-Assurance
Divisional business units are responsible for identifying, evaluating and managing the risks that originate within approved risk appetite and policies. They are required to establish and maintain appropriate risk management controls, resources and self-assurance processes.The 2nd Line of Defence - Establishment of Risk Management Frameworks and Policies and Risk Management Oversight
- Sector Audit Committees lead the optimisation of risk-reward by overseeing the development of risk appetite statements, risk management frameworks, policies and risk concentration controls, and monitoring Hayleys’ risk profile for alignment with approved appetites and strategies.
- Sector Management is responsible for developing division-specific risk appetite statements, policies, controls, procedures, monitoring and reporting capability, which align to the Board’s Statement of Risk Appetite and the risk management frameworks approved by the Board of Directors. These risk areas are independent of the Divisions’ 1st Line business areas, within the Group.
- Internal Audit has direct reporting line to the Sector Audit Committees as well as to the Hayleys PLC Audit Committee.
The 3rd Line of Defence - Independent Assurance
Our Group assurance function independently evaluates the adequacy and effectiveness of the Group’s overall risk management framework and controls.Enterprise Risk Management Process
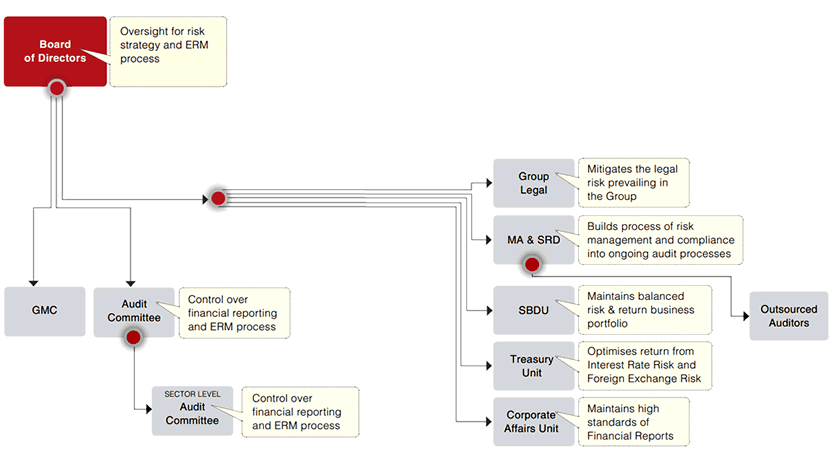
Risk Management Governance Structure
The principal aim of the Group’s risk management governance structure and system of Internal Control is to manage business and operational risks, with a view to enhancing the value of shareholders’ investments and safeguarding assets.We have put in place a number of key policies, processes and independent controls to provide assurance to the Board on the integrity of our reporting and effectiveness of our systems of Internal Control and risk management. The governance assurance diagram below highlights the relationship between the Board of Directors and the various controls in the assurance process. Some of the more significant Internal Control systems include Audit Committee, Sector Level Audit Committees, Hayleys Group Management Committee (HGMC), Treasury Unit (TU), Strategic Business Development Unit (SBDU), Group Legal & Management Audit & System Review Unit (MA&SRD).
Material Risks and their Impact
The SLFRS (Note 42 to the Financial Statements) deals with the details of financial risks and their management. Given below is a summary of other material risks faced by the Group in the short to medium term along with their impact, strategies and mitigating action and risk ratings.Impact of IFRS Convergence
Risk Rating: MODERATEWe have now come through the first-time adoption phase. Residual concerns hinge on any material impact on the financial performance, position and processes of the Group, which could affect decisions made by the users of Financial Statements.
To complete a smooth transition, the Hayleys Group has set up a special project - consisting of diagnostics and planning, solution development and implementation - that will ensure full compliance.
Information Technology
Risk Rating: MODERATEThe Group depends on accurate and timely information from key information technology (IT) and business intelligence systems to enable decision-making.
The implementation of a sound IT policy throughout the Group is supported by adequate systems and controls. A contingency plan is in place to mitigate the risk of IT failures and business recovery and continuity. A central IT team is in place to support IT within the Group.
Product Risk and Competition
Risk Rating: MODERATEGlobal mergers and acquisitions of principals which are commonplace, can lead to the loss of agencies held. The latter is particularly relevant for the consumer, agricultural inputs and products, industrial inputs and transportation segments of the Group’s business.
The presence of Group companies overseas and long-term relationships through a valued network of foreign and local business partners help identify risks and actions to mitigate these. Good principal - agent relationships reduce the risk of unexpected, adverse events. The Group remains alive to new market opportunities, to developing new alliances, and to acquiring distribution channels, which reduce the impact of any losses that do arise.
Hayleys remains strong in attracting FDIs and securing projects and joint ventures for business communities. In addition, the Group’s excellent close working relationships with international bodies have enhanced the standing of the Hayleys brand.
Raw Materials, Energy, Freight and other Operating Inputs
Risk Rating: MODERATEMargins in all our business sectors may be affected by fluctuations in the price of operating inputs. While many of these are factors beyond our control, such as weather and geopolitics, some are also due to the basis of pricing in sales contracts. Such risks are mitigated through our strategic relationships with suppliers that include multiple-source supply agreements for key inputs and a balanced portfolio of suppliers and customers. In addition, where possible, hedging mechanisms are used to manage exposure to movements in the future prices of commodities.
Employees and Human Resource Management
Risk Rating: MODERATEAn identified shortage of skilled labour and limitations in quality labour for outsourced requirements prove detrimental to a company’s sustainability. The impact of such a risk is felt quite strongly amongst many manufacturing and service oriented industries in Sri Lanka today.
The Hayleys Group focuses on talent attraction and retention in its action plans to mitigate this risk. We attract and retain quality employees through systems such as performance recognition and job banding, as well as training and development programmes for all levels.
Socio-economic Policies and Local Communities
Risk Rating: MODERATE/HIGHDue to increased costs within the country’s current socioeconomic framework there is a potential loss of competitiveness of our products in the international market place. Moves such as removal of protective tariffs for local produce or implementation of new regulations are identified as risks to multiple sectors. Hayleys addresses relevant economic issues with regulatory and other authorities and lobbies with them. In tandem, measures are taken to maximise productivity and reduce costs. For example, energy costs are mitigated by the use of alternative energy sources, while operations are established overseas to diversify a multitude of risks that include matters such as disruptions in the supply chain, climate change, changes in fiscal policies, law and order.
Unexpected societal risk that impacted on our licence to operate is a material concern that raised its head during the year in respect of our Hand Protection sector. It exposed weaknesses in the prevailing system, both internal and external, in addressing an unfounded allegation on an environmental issue that got blown out of proportion. The lessons learnt are being internalised across the Group.
Eco-friendly Products and Services
Risk Rating: MODERATEStronger environmental and health/safety legislation is visible in our buyers’ markets, which is a positive indication for the Hayleys Group.
The highest priority is given to maintaining close relationships with customers and responding to their needs. As a result product innovation is of vital importance. The Group innovates in the fields of public health, drought resistance, renewable energy resources, eco-friendly biodegradable products and purification solutions.
Certifications won by Hayleys, such as the world’s first Fair Trade rubber gloves and the first Ethical Tea Brand of the world provide immense opportunities globally where the focus is shifting towards ethical business practices and sustainability.
Environment and Climate Change
Risk Rating: MODERATEManufacturing and agriculture companies of the Group that use indigenous raw materials such as coconut fibre, coconut shell, latex and gherkins are affected by shortages due to weather conditions. Climate change affects quality standards as well as the quantity of supply of certain products and makes supply forecasting difficult.
The effects of macro forces on food security are seen through growth of pests and diseases caused by disruption of weather patterns and changes in temperature. Overall, changes in climatic conditions affect operations across the Group’s diversified manufacturing, agriculture or services portfolio.
The Group mitigates the risk of shortages in raw materials by building buffer stocks when raw materials are available. Group companies source from other countries as necessary and when feasible, geographically diversify our risks by establishing manufacturing units overseas.