 Content
Content
- Home
- Context
-
Management Report
- The Operating Environment...and Trends Refining Our Portfolio...and Reinventing Our Future Financial Value Creation Delivering Value to Customers...and their Value to Us Working at Dimo...Enjoyable and Rewarding Our Business Partners...A Symbiotic Relationship Regulatory Authorities...Playing by the Rules Our Community...Live and Let Live The Environment...Now and for Generations Yet Unborn Sustainability Performance Objectives in 2012/13
- Stewardship
-
Financial Reports
- Annual Report of the Board of Directors Statement of Directors' Responsibilities for the Financial Statements Independent Auditors' Report Income Statement and Statement of Comprehensive Income Statement of Financial Position Statement of Changes in Equity Cash Flow Statement Notes to the Financial Statements
- Appendices
- Downloads
- Likelihood of occurrence is assessed on the basis of past experience and the preventive measures in place. A ranking of high, medium and low in terms of the probability of occurrence is assigned for each risk.
- The impact of the event is assessed by determining the loss it would cause and the extent of the impact. By considering these two factors, the impact is then categorised as low, moderate and significant.
- Gradually strengthening non-vehicle-related areas of business such as marketing & distribution and engineering solutions in power, water, building technologies and healthcare sectors.
- Strict adherence to Group Credit Policy that includes evaluation of a customer prior to granting credit and credit administration.
- Periodic review of receivables by the Group Management Committee
- Draw up special schemes with vehicle financiers to offer competitive lease rentals
- Cautious management of working capital/prudent treasury management
- Maintain an appropriate combination of fixed and floating rate debt
- Hedging through forward contracts, where desirable
- In addition to the above, hedging of this impact is available to the extent that trade receivables in foreign currency and foreign currency bank account balances cover the exposure on foreign currency payables
- The finance and treasury functions ensure that banking facilities are in place to cover its forecasted cash needs for at least a period of twelve months
- The Group maintains a desired mixture of cash and cash equivalents
- Extensive controls and reviews to maintain integrity and efficiency of IT infrastructure and data
- Regular back up of data & off-site storage of data backup system
- Disaster recovery plan
- Significant investments have been made towards protecting the IT system from failures and security breaches
- Leverage information technology to manage inventory and ordering
- Periodic review of inventory age analysis
- Stocks age analysis
- Evaluation of slow moving stock on a regular basis with action plans reviewed by Business Unit Managers on a periodic basis.
- Preventive measures of safety are taken to minimise damage to people and property in the case of fire or floods
- The Company has a disaster recovery plan in place
- Indemnity from insurance policies
- The Group makes regular investments in new technology in providing after sales services and in IT infrastructure
- Staff are consistently exposed to new technology and trained to handle them
- The Group is backed by world renowned brands, some of whom are technology leaders. Therefore, technology is leveraged to compete with others
- Availability of a Quality Management Systems.
- Dedicated unit for Customer Relationship Management
- Continuous training of employees on customer care and aftercare
- Inclusion of customer care and customer satisfaction index in employees’ and business unit objectives.
- Due importance given to the human resources management function of the Group
- Top management involvement in talent management led by the Human Resources Department
- Adoption of Best Practices in human resources management
- Conducting employee satisfaction surveys
- Investment in training and development
- Policy of competitive remuneration
- An ‘Open door policy’ is in place to discuss grievances with superiors
- An employee council meets every month to provide for employee representation
- HR clinics are held at business locations where representatives from HR Department visit locations to listen to employee grievances.
- The Company has focused on developing a mutually beneficial relationship with principals in an effort to minimise the risk.
- Independent survey on expectations of principals
- Emphasis on meeting expectations of principals
- Periodic evaluation of Principals’ satisfaction levels
- A detailed account of our relationships with principals is given from pages 39 to 40.
- Feedback from principals
- There were no instances of involuntary severences of relationship with foreign principals during the year 2012/13 and 2011/12.
- The Code of Business Ethics of the Group requires that all employees comply with laws and regulations.
- A written undertaking is obtained from every employee, that the Code of Business Ethics will be followed by him/her. The Code requires that all employees comply with all laws applicable to the Group.
- Internal and independent assurance provides comfort on compliance with laws and regulations.
- Damage to the reputation and loss of stakeholders’ interest as a result of social rejection
- Loss of reputation arising from corporate behaviour against the interests of the society
- Engagement in various community related activities, including community development
- Philanthropy
- Developing the social and physical infrastructure of the community
- Upholding of the principles of Global Compact relating to social development.
- Environmental sustainability is a part of the decision making process in day to day operations and strategy formulation
- Existence of a sustainability committee to manage environmental sustainability related issues
- The Group’s Environmental Management System is accredited with ISO 14001:2004
- The Company follows GRI Guidelines on sustainability reporting. The GRI index is available in the Dimo Detailed Annual Report.
The Annual Report Company
Risk Management
Overview
The constantly evolving environment and the interactions with our stakeholders present the Company with risks and opportunities. In addition, the Group has to manage risks that arise from its operations. Thus, a need arises to identify and manage risks. The systematic approach required for risk management calls for measures that ensure that risks are identified on time, evaluated in terms of risk appetite of the Group and effective management and monitoring mechanisms are installed.
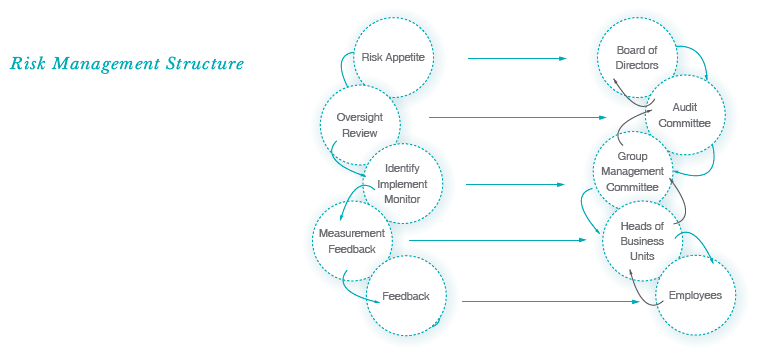
Risk Management Structure
The Board is primarily responsible for ensuring that the risks are identified and appropriately managed across the Group. The Audit Committee has been delegated the responsibility for reviewing the effectiveness of the Group’s Risk Management process, including the systems established to identify, assess, manage and monitor risks. The Internal Audit function also plays a key role in risk identification.
The Group Management Committee (GMC) takes the lead at the implementation level in identifying risks. The GMC examines processes and events that expose the Company into situations that could seriously reduce earnings, impair its liquidity position or create legal, regulatory or reputation risks. The GMC also evaluates options available to mitigate risks and to identify risks that do not match the risk appetite of the Group. Monitoring of risk management measures is a responsibility that rests with the GMC.
Heads of Business Units provide useful information and feed back to the GMC for risk management with the assistance of the employees of the Group
Risk Evaluation
Where a risk is evaluated it takes into account the likelihood of an event and its potential impact on the business. Impacts are quantified or assessed in terms of potential loss or damage. Risks are assessed both as gross risk and net risk. The assessment of gross risk involves the potential harm it can cause without mitigating actions, whereas net risk assessment considers potential harm or loss when mitigating action is taken. Risks and their corresponding mitigating action plans are reviewed by the GMC.
Risk Mapping
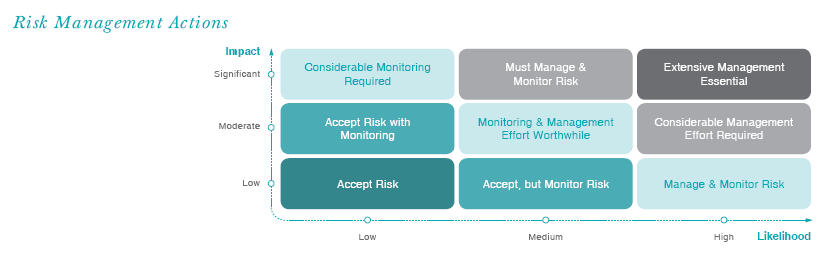
Risk mapping is carried out in order to assess the likelihood of occurrence and consequences of an event/set of events:
Upon assessment of the likelihood of occurrence and the extent of the impact of each risk, it is subjected to the following matrix in order to derive the nature and intensity of action required.
Risk Management Actions
The table given below sets out an assessment of risks that the strategic imperatives were subject to towards the year-end and risk mitigating actions that were/are in place:
Strategic Imperatives and Associated Risks
| Strategic Imperative 1 | Refine the Portfolio Mix of Our Business Continuously | |||||||||
| Risk factor/implications | Composition of product portfolio: The vehicles and vehicle parts/services segment accounts for a significant share of Group’s revenues and negative changes to the fiscal policies would adversely impact on Group’s performance. | |||||||||
| Key controls and mitigating actions |
||||||||||
| Monitoring indicators |
|
|||||||||
| Risk assessment | Extensive management essential |
| Strategic Imperative 2 | Create Financial Value | |||||||||||||||
| Risk factor/implications | Credit risk - Possibility of incurring bad debts due to adverse economic conditions/poor credit management | |||||||||||||||
| Key controls and mitigating actions |
||||||||||||||||
| Monitoring indicators |
|
|||||||||||||||
| Risk assessment | Manage and monitor risk | |||||||||||||||
| Risk factor/implications | Interest rate risk - Increase in interest rates impacting vehicle sales and Company’s cost of funding | |||||||||||||||
| Key controls and mitigating actions |
||||||||||||||||
| Monitoring indicators |
|
|||||||||||||||
| Risk assessment | Manage and Monitor risk | |||||||||||||||
| Risk factor/implications | Exchange rate fluctuation risk - fluctuations in exchange rates causing potential losses on assets & liabilities and transactions denominated in foreign currency | |||||||||||||||
| Key controls and mitigating actions |
||||||||||||||||
| Monitoring indicators |
|
|||||||||||||||
| Risk assessment | Manage and monitor risk | |||||||||||||||
| Risk factor/implications | Liquidity risk - Unavailability of sufficient funds impacting smooth functioning of the day-to-day operations of the Company | |||||||||||||||
| Key controls and mitigating actions |
||||||||||||||||
| Monitoring indicators |
|
|||||||||||||||
| Risk assessment | Considerable monitoring required | |||||||||||||||
| Risk factor/implications | IT - related risk - Loss of business/reputation resulting from break-down of IT systems and/or access by unauthorised personnel | |||||||||||||||
| Key controls and mitigating actions |
||||||||||||||||
| Monitoring indicators |
|
|||||||||||||||
| Risk assessment | Considerable monitoring required | |||||||||||||||
| Risk factor/implications | Obsolescence of inventory - Losses resulting from slow moving inventory items becoming obsolete | |||||||||||||||
| Key controls and mitigating actions |
||||||||||||||||
| Monitoring indicators | ||||||||||||||||
| Risk assessment | Accept, but monitor risk | |||||||||||||||
| Risk factor/implications | Natural disasters - damages resulting from natural disasters such as fire and floods | |||||||||||||||
| Key controls and mitigating actions |
||||||||||||||||
| Monitoring indicators |
|
|||||||||||||||
| Risk assessment | Considerable monitoring required | |||||||||||||||
| Risk factor/implications | Technological obsolescence - Loss of business and cost of being inefficient due to non-availability of latest technology | |||||||||||||||
| Key controls and mitigating actions |
||||||||||||||||
| Monitoring indicators |
|
|||||||||||||||
| Risk assessment | Existence of risk is inevitable and requires monitoring |
| Strategic Imperative 3 | Earn the Trust of Customers and They Keep Coming Back | |||||||||
| Risk factor/implications | Loss of customer relationships - Loss of customers and resulting impact on business due to dissatisfied customers. | |||||||||
| Key controls and mitigating actions |
||||||||||
| Monitoring indicators |
|
|||||||||
| Risk assessment | Monitoring and management effort worthwhile |
| Strategic Imperative 4 | Nurture People and They Find it Enjoyable and Rewarding to Work with Us | |||||||||
| Risk factor/implications | Sourcing and retaining suitable human resources - Adverse impacts arising from failure to recruit/retain skilled employees | |||||||||
| Key controls and mitigating actions |
||||||||||
| Monitoring indicators |
|
|||||||||
| Risk assessment | Accepting the risk is inevitable. Monitoring required | |||||||||
| Risk factor/implications | Labour relations - Losses from low productivity and low employee engagement as a result of industrial disputes | |||||||||
| Key controls and mitigating actions |
||||||||||
| Monitoring indicators | There were no industrial disputes during the financial years 2012/13 and 2011/12 | |||||||||
| Risk assessment | Considerable monitoring required |
| Strategic Imperative 5 | Have Great Relationships with Best-of-Breed Business Partners |
| Risk factor/implications | Relationships with principals - Performance being adversely impacted as a result of disruptions to relationships with principals. |
| Key controls and mitigating actions |
|
| Monitoring indicators | |
| Risk assessment | Considerable monitoring required |
| Strategic Imperative 6 | Play by the Rules |
| Risk factor/implications | Non-compliance with laws and regulations - Potential exposure of the Company to financial losses, litigation and unacceptable corporate behaviour. |
| Key controls and mitigating actions |
|
| Monitoring indicators | There were no material non-compliance reported during the year ended 2012/13 and 2011/12. |
| Risk assessment | Considerable monitoring required. |
| Strategic Imperative 7 | Serve the Community | ||||||
| Risk factor/implications | Social risk -
|
||||||
| Key controls and mitigating actions |
|||||||
| Monitoring indicators |
|
||||||
| Risk assessment | Risk may be worth, accepting with monitoring. |
| Strategic Imperative 8 | Be Friendly Towards the Environment | ||||||
| Risk factor/implications | Environmental risk - Loss of confidence/business opportunities/depletion of Company image due to Company not being perceived as a responsible citizen. | ||||||
| Key controls and mitigating actions | |||||||
| Monitoring indicators |
|
||||||
| Risk assessment | Risk is inevitable and requires monitoring |